I ntegrated Pest Management or IPM, as it is commonly known, is a system of managing pests which is designed to be sustainable. IPM involves using the best combination of cultural, biological and chemical measures for particular circumstances, including plant biotechnology as appropriate. This provides the most cost effective, environmentally sound and socially acceptable method of managing diseases, insects, weeds and other pests in agriculture.
The plant science industry has endorsed IPM practices for many years, and has publicly declared its commitment to promoting IPM. All CropLife International member companies support and abide by the definition of IPM in the International Code of Conduct on Pesticide Management (Article 2): “Integrated Pest Management (IPM) means the careful consideration of all available pest control techniques and subsequent integration of appropriate measures that discourage the development of pest populations and keep pesticides and other interventions to levels that are economically justified and reduce or minimize risks to human health and the environment. IPM emphasizes the growth of a healthy crop with the least possible disruption to agro ecosystems and encourages natural pest control mechanisms.”
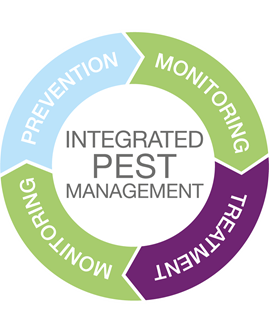
IPM is a flexible approach which makes the best use of all available technologies to manage pest problems effectively and safely. IPM strategies consist of three basic components:Please see here the latest video on IPM.
An elementary principle of effective IPM is to develop pest control strategies that take into account all relevant control tactics and locally available methods, and are sensitive to local environment and social needs. The successful user of IPM will evaluate the potential cost effectiveness of each alternative as well as the whole control strategy. See infographic on IPM here. Elements that can be included in an IPM program are summarized in the figure below.
The plant science industry, represented by CropLife International, provides a wide range of appropriate technologies, services and products that can be incorporated into IPM strategies. Additionally, IPM principles are included in industry training programs for farmers and other stakeholders across the world. A number of training and information documents have been produced to support these programs, including a web-based training program – aglearn.net –which has modules on IPM principles, cotton IPM, rice IPM and vegetable IPM. Ultimately, development and adoption of IPM strategies requires mutual support and collaboration from a range of stakeholders, including government and non-government organizations, international research organizations, distributors, dealers and retailers, and farmers themselves.
Further information on IPM can be downloaded as a leaflet here and as a brochure here. Case studies are available here, and an IPM training manual is available here.

